Table of Contents
Manufacturing Business Definition
A manufacturing business is any business that uses components, parts, or raw materials to make a finished good. These finished products can be sold directly to consumers or to other manufacturing companies that use them to make a different products. Manufacturing companies in today’s world are typically made up of machines, robots, computers, and humans that work in a specific way to create a product.
Manufacturing plants often use an assembly line, a process in which a product is assembled in sequence from one workstation to the next. By moving the product down an assembly line, the finished product can be built faster with less manual labour.
What is Manufacturing?
Manufacturing is the creation of goods by hand or by mechanism, which, after completion, are sold to a buyer. Items used in manufacturing may be raw materials or parts of a larger product. Manufacturing usually happens on a large-scale machine production line and with skilled labour.
Examples of Manufacturing Business
The crossing is one of the top automakers in the US and has been building vehicles on a large scale since the early 20th century. Assembly lines are a great visual of what a manufacturing company does. Ford can easily make over five million cars in a single year.
If you like brown, you may want to travel to Hershey, Pennsylvania, home of the Hershey Company. Hershey’s has been manufacturing its famous chocolate bars at various plants in the United States and Mexico for more than 100 years. Some plants produce products like Kit Kats, Reese’s Peanut Butter Cups, Whoppers, Rolos, and Twizzlers.
Types of Manufacturing Business

Manufacturing is a specific business; the owner purchases the raw material or parts and manufactures the final product. To purpose as a business, the manufacturer needs to collect costs, know the demand, and make a product.
A factory functions in one of three types of manufacturing production:
Supply Merchandise: A factory produces goods to supply stores and showrooms. And also, the manufacturer will plan the production activity if they anticipate the market for their interests. And also if they overproduce, they may need to sell the surplus at a loss, and if they don’t produce enough, they may lose the market and not sell enough to cover costs.
Order to make: And also, the producer waits for the orders before manufacturing the merchandise. Thus the inventory is easier to control, and the owner does not need to depend so much on the market. Customer waiting time is longer even though the manufacturer requires a constant flow of orders to keep the factory producing.
Assemble to Make: The factory produces the parts before the orders are assembled. In this way, the manufacturer is ready to fulfil customer orders, but the producer will have merchandise from unwanted details of the charges that do not materialise.
Process of Manufacturing Business
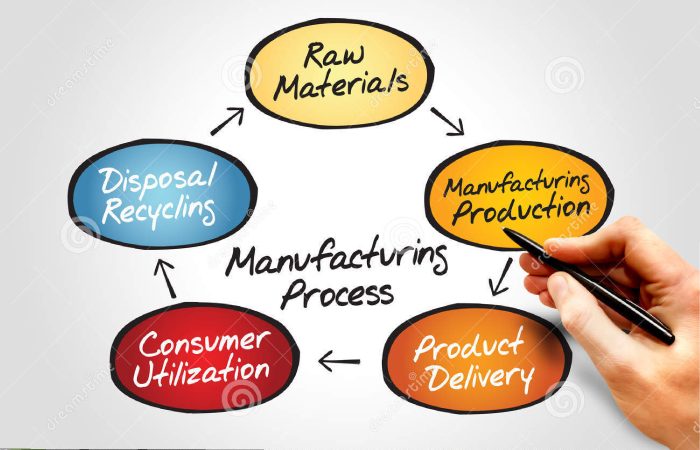
Technically, the manufacturer works with raw materials to obtain a complete and commercially viable product. Trendsetting Manufacturing technology predominantly governs the entire business.
Additive manufacturing is a process that involves joining two materials together. And also, the most prevalent is rapid prototyping which assembles the physical parts using 3D Computer-Aided Design (CAD) data. Other techniques include laser sintering and 3D printing.
Software: Manufacturers use business automation and inventory management tools that help them in material requirements planning, inventory control and proper accounting. Aside from that, these systems automate custom quotes for high-end customers, manage orders, and process all purchases from wholesalers. A large-scale manufacturer uses elite software that is powerful enough to handle financial and warehouse management quite accurately.
Automated Systems: This is a great move to produce good quality goods and constantly speeds up the entire process. Remember, ultimately, supply must meet demand. And also,the systems use artificial intelligence that only manufacturers depend on to make wise decisions about optimizing their business objectives. Nowadays, assembly systems and conveyor belts in the manufacturing sector prove to be a great advantage in fulfilling all tasks.
The Distinction between Manufacturers, Wholesalers, Retailers and Distributors.
In the best possible way, these terms are very closely related. On the other hand, a clear line needs to draw. A wholesaler in this line of business is more or less an intermediary between the distributor and the retailers.
So why is it wise to work with wholesalers? They make the entire distribution chain complete. Also, they can get products from different distributors. In other words, they fulfil orders placed by retailers.
Ideally, Distributors Work hand in hand with manufacturers. There must be a very strong business relationship between the two parties for this to prevail. Most of the time, both counterparties enter into legal agreements so that all transactions are formal and successful. In addition, manufacturers may supply products to distributors on credit.
How to Mitigate Manufacturing Business Risks?
For starters, a manufacturer must defend against supply chain risk. And also, it happens when providers are not reliable enough. This prevents you from getting your products to the final buyer. Keep track of all the necessary raw materials that come in handy when placing an order. In that sense, a manufacturer must outsource components from well-founded suppliers. One that can deliver on its promise by beating all deadlines.
There are operational risks that occur in the entire production process. A manufacturer must set aside money to replace machines that might break or depreciate in the long run. A backup power supply is something you should consider.
Build Your Customer Relationships

If you are a manufacturer who sells your products wholesale or direct to consumer, you need to foster relationships with your customers.
By providing excellent customer service, listening to customer feedback, and offering excellent quality products, you can build valuable relationships that will continue to grow your business for years to come.
Because It Is Important
Manufacturing is crucial for producing and delivering goods to the market and is also essential for economic reasons. In the United States, for example, manufacturing accounts for 15% of economic output. The mass production of items can boost the economy, measured by “manufacturing value added (MVA)” indicators. These compare manufacturing production to the size of the overall economy to make a percentage of gross domestic product (GDP). Manufacturing employment, inventory, and order numbers are scrutinized by manufacturing institutes, such as The Institute for Supply Management (ISM), whose reports inform financial analysts and researchers.
Conclusion
A manufacturer is a registered person or company that makes finished products from raw materials for profit. And also, the products are further distributed to wholesalers and retailers, who then sell to customers. Retailers display products through physical or third-party stores—e-commerce platforms. In the manufacturing industry, products manufacture on a large scale to meet the irresistible demand of consumers.


